The SEAS Smart Meter ontology
- This version: v1.0 - https://w3id.org/seas/SmartMeterOntology-1.0
- Latest published version: https://w3id.org/seas/SmartMeterOntology
- Creators:
- Lynda TEMAL
-
Contributors:
-
Issued: 2016-05-10
- Modified: 2016-11-24
- Imports: CommunicationOntology, DeviceOntology , ElectricPowerSystemOntology
- Other visualizations: VOWL, Turtle, RDF/XML.
The SEAS Smart Meter ontology defines seas:SmartMeter as physical system (seas:Sensor) that are designed to Compute Metering on different amount of matter, such as Natural Gas, Water and Electricity. Smart Meters are connected systems which are able to send metering evaluation to some managing systems. In the current version Smart meter are composed (seas:subsystemOf) of a traditional meter and a connector module which is connected to the meter. The two systems form the smartMeter. In this ontology you will find concepts about - Meters (seas:WaterMeter, seas:GasMeter, seas:ElectricityMeter) and their metering mechanism (seas:PulseMetering, seas:OpticMetering, seas:DiscMetering..). - Connectors module, these connectors can communicate thanks to a - seas:CommunicationDevice such as seas:LoraCommunicationDevice and seas:SigFoxCommunicationDevice. Figure below shows the taxonomy of Meter. 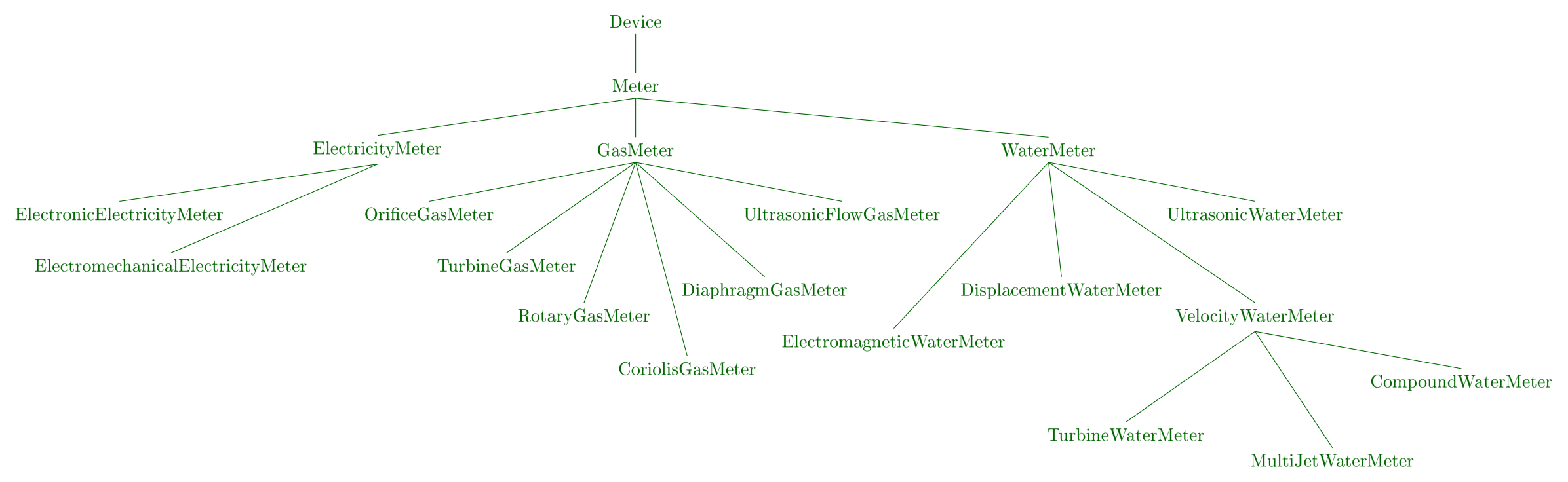
Classes
CompoundWaterMeter
Label: Compound Water Meter
IRI: https://w3id.org/seas/CompoundWaterMeter
A compound water meter is used where high flow rates are necessary, but where at times there are also smaller rates of flow that need to be accurately measured. Compound meters have two measuring elements and a check valve to regulate flow between them. At high flow rates, water is normally diverted primarily or completely to the high flow element. The high flow element is typically a turbine meter. When flow rates drop to where the high flow element cannot measure accurately, a check valve closes to divert water to a smaller element that can measure the lower flow rates accurately. The low flow element is typically a multi-jet or PD meter. By adding the values registered by the high and low elements, the utility has a record of the total consumption of water flowing through the meter. (Source: Wikipedia)
-
sub class of: VelocityWaterMeter
ConsumptionEvaluation
Label: Consumption Evaluation
IRI: https://w3id.org/seas/ConsumptionEvaluation
The class of evaluations for consumption properties.
- sub class of: Evaluation
ConsumptionMetering
Label: Consumption Metering
IRI: https://w3id.org/seas/ConsumptionMetering
Any metering about some consumption.
- sub class of: Metering
ConsumptionMeteringExecution
Label: Consumption Metering Execution
IRI: https://w3id.org/seas/ConsumptionMeteringExecution
A Consumption Metering Execution is the execution of some Consumption metering implemented by some meter.
- sub class of: MeteringExecution
ConsumptionProperty
Label: Consumption Property
IRI: https://w3id.org/seas/ConsumptionProperty
The consumption property is a property to measure any consumption.
- sub class of: Property
- range of: consumption
CoriolisGasMeter
Label: Coriolis Gas Meter
IRI: https://w3id.org/seas/CoriolisGasMeter
A coriolis meter is usually one or more pipes with longitudinally or axially displaced section(s) that are excited to vibrate at resonant frequency. Coriolis meters are used with liquids and gases. When the fluid within the displaced section is at rest, both the upstream and downstream portion of the displaced section will vibrate in phase with each other. The frequency of this vibration is determined by the overall density of the pipe (including its contents). This allows the meter to measure the flowing density of the gas in real time. Once the fluid begins to flow, however, the coriolis effect comes into play. This effect implies a relationship between the phase difference in the vibration of the upstream and downstream sections and the mass flow rate of the fluid contained by the pipe. (Source: Wikipedia)
- sub class of: GasMeter
DiaphragmGasMeter
Label: Diaphragm Gas Meter
IRI: https://w3id.org/seas/DiaphragmGasMeter
Diaphragm Gas Meter are the most common type of gas meter, seen in almost all residential and small commercial installations. Within the meter there are two or more chambers formed by movable diaphragms. With the gas flow directed by internal valves, the chambers alternately fill and expel gas, producing a near continuous flow through the meter. As the diaphragms expand and contract, levers connected to cranks convert the linear motion of the diaphragms into rotary motion of a crank shaft which serves as the primary flow element. This shaft can drive an odometer-like counter mechanism or it can produce electrical pulses for a flow computer. (Source: Wikipedia)
- sub class of: GasMeter
DiscMetering
Label: Disc Metering
IRI: https://w3id.org/seas/DiscMetering
Disc Metering is a Metering which use the disc methods to measure the property.
- sub class of: Metering
DisplacementWaterMeter
Label: Displacement Water Meter
IRI: https://w3id.org/seas/DisplacementWaterMeter
Displacement water meters are most often used in residential and small commercial applications and homes. Displacement meters are commonly referred to as Positive Displacement, or “PD” meters.
Two common types are oscillating piston meters and nutating disk meters. Either method relies on the water to physically displace the moving measuring element in direct proportion to the amount of water that passes through the meter. The piston or disk moves a magnet that drives the register. (Source: Wikipedia)
- sub class of: WaterMeter
ElectricityMeter
Label: Electricity Meter
IRI: https://w3id.org/seas/ElectricityMeter
An electricity meter, electric meter, electrical meter, or energy meter is a meter that measures the amount of electric energy consumed by a residence, a business, or an electrically powered device. (Source: Wikipedia)
- sub class of: Meter
ElectricityMetering
Label: Electricity Metering
IRI: https://w3id.org/seas/ElectricityMetering
The Measure of the electricity which flow through the meter device. It Could be a metering about a consumption or a production of the electricity
- sub class of: Metering
ElectricityMeteringExecution
Label: Electricity Metering Execution
IRI: https://w3id.org/seas/ElectricityMeteringExecution
An Electricity Metering Execution is the execution of some Electricity Metering process by some electricity meter.
- sub class of: MeteringExecution
ElectromagneticWaterMeter
Label: Electromagnetic Water Meter
IRI: https://w3id.org/seas/ElectromagneticWaterMeter
Magnetic flow water meters, commonly referred to as “mag meters”, are technically a velocity-type water meter, except that they use electromagnetic properties to determine the water flow velocity, rather than the mechanical means used by jet and turbine meters. Mag meters use the physics principle of Faraday’s law of induction for measurement, and require AC or DC electricity from a power line or battery to operate the electromagnets. (Source: Wikipedia)
- sub class of: WaterMeter
ElectromechanicalElectricityMeter
Label: Electromechanical Electricity Meter
IRI: https://w3id.org/seas/ElectromechanicalElectricityMeter
The most common type of electricity meter is the electromechanical induction watt-hour meter. The electromechanical induction meter operates by counting the revolutions of a non-magnetic, but electrically conductive, metal disc which is made to rotate at a speed proportional to the power passing through the meter. The number of revolutions is thus proportional to the energy usage. (Source: Wikipedia)
- sub class of: ElectricityMeter
ElectronicElectricityMeter
Label: Electronic Electricity Meter
IRI: https://w3id.org/seas/ElectronicElectricityMeter
Electronic meters display the energy used on an LCD or LED display, and some can also transmit readings to remote places. In addition to measuring energy used, electronic meters can also record other parameters of the load and supply such as instantaneous and maximum rate of usage demands, voltages, power factor and reactive power used etc. They can also support time-of-day billing, for example, recording the amount of energy used during on-peak and off-peak hours. (Source: Wikipedia)
- sub class of: ElectricityMeter
FrequencyEvaluation
Label: Frequency Evaluation
IRI: https://w3id.org/seas/FrequencyEvaluation
The class of evaluations for frequency properties.
- sub class of: Evaluation
FrequencyProperty
Label: Frequency Property
IRI: https://w3id.org/seas/FrequencyProperty
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time.
- sub class of: Property
- range of: evaluationFrequency, frameSendingFrequency , samplingMeasuringFrequency
GasMeter
Label: Gas Meter
IRI: https://w3id.org/seas/GasMeter
A gas meter is a meter, used to measure the volume of fuel gases such as natural gas and propane. Gas meters are used at residential, commercial, and industrial buildings that consume fuel gas supplied by a gas utility. (Source: Wikipedia)
- sub class of: Meter
GasVolumeEvaluation
Label: Gas Volume Evaluation
IRI: https://w3id.org/seas/GasVolumeEvaluation
The class of evaluations for Gas volume properties.
- sub class of: VolumeEvaluation
GasVolumeMetering
Label: Gas Volume Metering
IRI: https://w3id.org/seas/GasVolumeMetering
The Measure of the volume of the gas which flow in the meter. Generally for consumption metering.
- sub class of: Metering
GasVolumeMeteringExecution
Label: Gas Volume Metering Execution
IRI: https://w3id.org/seas/GasVolumeMeteringExecution
The Measure of the volume of the gas which flow in the meter. Generally for consumption metering but could be for production.
- sub class of: MeteringExecution
GasVolumeProperty
Label: Gas Volume Property
IRI: https://w3id.org/seas/GasVolumeProperty
The Gas Volume is a property inherent in Gas. Could be computed in litre or in meter cube.
- sub class of: VolumeProperty
InstallingDateMeterIndexEvaluation
Label: Installing Date Meter Index Evaluation
IRI: https://w3id.org/seas/InstallingDateMeterIndexEvaluation
The class of evaluations for meter index properties at installing date.
- sub class of: MeterIndexEvaluation
Meter
Label: Meter
IRI: https://w3id.org/seas/Meter
A Meter is a device that is designed to allow to carry out a metering process.
- sub class of: Device
- domain of: evaluationFrequency, meterIndex , samplingMeasuringFrequency
MeterIndexEvaluation
Label: Meter Index Evaluation
IRI: https://w3id.org/seas/MeterIndexEvaluation
The class of evaluations for meter index properties.
- sub class of: Evaluation
MeterIndexProperty
Label: Meter Index Property
IRI: https://w3id.org/seas/MeterIndexProperty
The Meter index property is a property which is inherent in the Index of the Meter.
- sub class of: Property
- range of: meterIndex
Metering
Label: Metering
IRI: https://w3id.org/seas/Metering
Metering is the process that allows to carry out some measuring on a property.
- sub class of: https://w3id.org/pep/Process
MeteringExecution
Label: Metering Execution
IRI: https://w3id.org/seas/MeteringExecution
A Metering Execution is the execution of the measuring process which is executed by a meter device.
- sub class of: https://w3id.org/pep/ProcessExecution
MultiJetWaterMeter
Label: Multi-jet Water Meter
IRI: https://w3id.org/seas/MultiJetWaterMeter
Multi-jet meters are very accurate in small sizes and are commonly used for residential and small commercial users. Multi-jet meters use multiple ports surrounding an internal chamber to create multiple jets of water against an impeller, whose rotation speed depends on the velocity of water flow. Multi-jets are very accurate at low flow rates, but there are no large size meters since they do not have the straight-through flow path needed for the high flow rates used in large pipe diameters. (Source: Wikipedia)
- sub class of: VelocityWaterMeter
OpticMetering
Label: Optic Metering
IRI: https://w3id.org/seas/OpticMetering
Optic Metering is a Metering which use the optic methods to measure the property.
- sub class of: Metering
OrificeGasMeter
Label: Orifice Gas Meter
IRI: https://w3id.org/seas/OrificeGasMeter
An orifice gas meter consists of a straight length of pipe inside which a precisely known orifice creates a pressure drop, thereby affecting flow. Orifice meters are a type of differential meter, all of which infer the rate of gas flow by measuring the pressure difference across a deliberately designed and installed flow disturbance. The gas static pressure, density, viscosity, and temperature must be measured or known in addition to the differential pressure for the meter to accurately measure the fluid. Orifice meters often do not handle a large range of flow rates. They are however accepted and understood in industrial applications since they are easy to field-service and have no moving parts. (Source: Wikipedia)
- sub class of: GasMeter
ProductionEvaluation
Label: Production Evaluation
IRI: https://w3id.org/seas/ProductionEvaluation
The class of evaluations for production properties.
- sub class of: Evaluation
ProductionMetering
Label: Production Metering
IRI: https://w3id.org/seas/ProductionMetering
Any metering about some production.
- sub class of: Metering
ProductionMeteringExecution
Label: Production Metering Execution
IRI: https://w3id.org/seas/ProductionMeteringExecution
A Production Metering Execution is the execution of some Production Metering implemented by some meter.
- sub class of: MeteringExecution
ProductionProperty
Label: Production Property
IRI: https://w3id.org/seas/ProductionProperty
The production property is a property to measure any production.
- sub class of: Property
- range of: production
PulseMetering
Label: Pulse Metering
IRI: https://w3id.org/seas/PulseMetering
Pulse Metering is a Metering which uses the pulse methods to measure the property.
- sub class of: Metering
RotaryGasMeter
Label: Rotary Gas Meter
IRI: https://w3id.org/seas/RotaryGasMeter
Rotary gas meters are highly machined precision instruments capable of handling higher volumes and pressures than diaphragm meters. Within the meter, two figure “8” shaped lobes, the rotors (also known as impellers or pistons), spin in precise alignment. With each turn, they move a specific quantity of gas through the meter. The operating principle is similar to that of a Roots blower. The rotational movement of the crank shaft serves as a primary flow element and may produce electrical pulses for a flow computer or may drive an odometer-like counter. (Source: Wikipedia)
- sub class of: GasMeter
SmartMeter
Label: Smart Meter
IRI: https://w3id.org/seas/SmartMeter
A smart meter is a Meter that implements a metering and records a specific property at regular frequency, and also a CommunicationDevice that communicates this data regularly back to the utility for monitoring and billing.
- domain of: frameSendingFrequency, hasInstallationDate
TurbineGasMeter
Label: Turbine Gas Meter
IRI: https://w3id.org/seas/TurbineGasMeter
Turbine gas meters infer gas volume by determining the speed of the gas moving through the meter. Because the volume of gas is inferred by the flow, it is important that flow conditions are good. A small internal turbine measures the speed of the gas, which is transmitted mechanically to a mechanical or electronic counter. These meters do not impede the flow of gas, but are limited at measuring lower flow rates. (Source: Wikipedia)
- sub class of: GasMeter
TurbineWaterMeter
Label: Turbine Water Meter
IRI: https://w3id.org/seas/TurbineWaterMeter
Turbine water meters are less accurate than displacement and jet meters at low flow rates, but the measuring element does not occupy or severely restrict the entire path of flow. The flow direction is generally straight through the meter, allowing for higher flow rates and less pressure loss than displacement-type meters. They are the meter of choice for large commercial users, fire protection and as master meters for the water distribution system. (Source: Wikipedia)
- sub class of: VelocityWaterMeter
UltrasonicFlowGasMeter
Label: Ultrasonic flow Gas Meter
IRI: https://w3id.org/seas/UltrasonicFlowGasMeter
Ultrasonic flow gas meters are more complex than meters that are purely mechanical, as they require significant signal processing and computation capabilities. Ultrasonic meters measure the speed of gas movement by measuring the speed at which sound travels in the gaseous medium within the pipe. (Source: Wikipedia)
- sub class of: GasMeter
UltrasonicWaterMeter
Label: Ultrasonic Water Meter
IRI: https://w3id.org/seas/UltrasonicWaterMeter
Ultrasonic water meters use one or more ultrasonic transducer to send ultrasonic sound waves through the fluid to determine the velocity of the water. Since the cross-sectional area of the meter body is a fixed and known value, when the velocity of water is detected, the volume of water passing through the meter can be calculated with very high accuracy. Because water density changes with temperature, most ultrasonic water meters also measure the water temperature as a component of the volume calculation. (Source: Wikipedia)
- sub class of: WaterMeter
VelocityWaterMeter
Label: Velocity Water Meter
IRI: https://w3id.org/seas/VelocityWaterMeter
A velocity-type water meter measures the velocity of flow through a meter of a known internal capacity. The speed of the flow can then be converted into volume of flow to determine the usage. There are several types of meters that measure water flow velocity, including jet meters (single-jet and multi-jet), turbine meters, propeller meters and mag meters. Most velocity-based meters have an adjustment vane for calibrating the meter to the required accuracy. (Source: Wikipedia)
- sub class of: WaterMeter
VolumeEvaluation
Label: Volume Evaluation
IRI: https://w3id.org/seas/VolumeEvaluation
The class of evaluations for volume properties.
- sub class of: Evaluation
VolumeProperty
Label: Volume Property
IRI: https://w3id.org/seas/VolumeProperty
The Volume is a property which is inherent to a physical entity. That measure the quantity in three dimensional space.
- sub class of: Property
WaterMeter
Label: Water Meter
IRI: https://w3id.org/seas/WaterMeter
A water meter is a Meter designed to measure the quantity of water that flows through a pipe. The water meter can measures water consumption or water supply. Every seas:WaterMeter implements a specific metering method such as seas:PulseMetering,seas:DiscMetering, seas:DiscMetering, which allow them to measure the volume of water (seas:WaterVolume) that flow in the pipe. (Source: Wikipedia)
- sub class of: Meter
WaterVolumeEvaluation
Label: Water Volume Evaluation
IRI: https://w3id.org/seas/WaterVolumeEvaluation
The class of evaluations for water volume properties.
- sub class of: VolumeEvaluation
WaterVolumeMetering
Label: Water Volume Metering
IRI: https://w3id.org/seas/WaterVolumeMetering
The Measure of the volume of the water which flow in the meter
- sub class of: Metering
WaterVolumeMeteringExecution
Label: Water Volume Metering Execution
IRI: https://w3id.org/seas/WaterVolumeMeteringExecution
A Water Volume Metering Execution is the execution of some Water Volume Metering implemented by some Water Meter.
- sub class of: MeteringExecution
WaterVolumeProperty
Label: Water Volume Property
IRI: https://w3id.org/seas/WaterVolumeProperty
The Water Volume is a property inherent in water. Could be computed in litre or in meter cube.
-
sub class of: VolumeProperty
Object Properties
consumption
Label: consumption
IRI: https://w3id.org/seas/consumption
A production relationship connects an entity to its consumption property.
- sub property of: hasProperty
- domain: FeatureOfInterest
-
range: ConsumptionProperty
evaluationFrequency
Label: evaluation frequency
IRI: https://w3id.org/seas/evaluationFrequency
An evaluation frequency relationship connects an entity to the frequency between two successive evaluations given by the entity
- sub property of: frequency
- domain: Meter
- range: FrequencyProperty
frameSendingFrequency
Label: frame Sending Frequency
IRI: https://w3id.org/seas/frameSendingFrequency
A frame sending frequency relationship connects an entity to the frequency between two successive sending of frames by the entity
- sub property of: frequency
- domain: SmartMeter
- range: FrequencyProperty
measures
Label: measures
IRI: https://w3id.org/seas/measures
Links a metering, meter, or metering execution, to the feature of interest a property of which it measures.
If x measures a property, then it also measures the feature of interest of this property:
seas:measures < seas:measuresProperty o seas:isPropertyOf .
If a metering measures a feature of interest, then any meter that implements this metering also measures this feature of interest, and any metering execution that used this metering also measures this feature of interest. Furthermore, if a meter measures a feature of interest, then any Metering Execution executed by this meter also measures this feature of interest:
seas:measures < pep:implements o seas:measures . seas:measures < pep:methodUsed o seas:measures . seas:measures < pep:executedBy o seas:measures .
- range: FeatureOfInterest
measuresProperty
Label: measures property
IRI: https://w3id.org/seas/measuresProperty
Links a Metering, meter, or metering execution, to a property it measures.
If a Metering measures a property, then any meter that implements this Metering also measures this property, and any MeteringExecution that used this Metering also measures this property. Furthermore, if a meter measures a property, then any metering execution executed by this meter also measures this property:
seas:measuresProperty < pep:implements o seas:measuresProperty . seas:measuresProperty < pep:methodUsed o seas:measuresProperty . seas:measuresProperty < pep:executedBy o seas:measuresProperty .
- range: Property
meterIndex
Label: meter index
IRI: https://w3id.org/seas/meterIndex
Links the meter to its index property.
- sub property of: hasProperty
- domain: Meter
- range: MeterIndexProperty
production
Label: production
IRI: https://w3id.org/seas/production
A production relationship connects an entity to its production property.
- sub property of: hasProperty
- domain: FeatureOfInterest
- range: ProductionProperty
samplingMeasuringFrequency
Label: sampling measuring frequency
IRI: https://w3id.org/seas/samplingMeasuringFrequency
A sampling measuring frequency relationship connects an entity to the frequency between two successives sampling measuring made by the entity
- sub property of: frequency
- domain: Meter
-
range: FrequencyProperty
Data Properties
hasInstallationDate
Label: has installation date
IRI: https://w3id.org/seas/hasInstallationDate
- domain: SmartMeter
- range: http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#dateTime


